Soapstone is talc with some impurities in it.
It is called soapstone because it is slippery like soap.
Tigers eye
Tiger’s Eye is a quartz that contains fibers of crocidolite which has altered to a yellow color.
It is formed by the alteration of crocidolite and consists essentially of quartz colored by iron oxide.
The fibers give the specimen it’s distinctive glowing chatoyancy.
Tiger's eye is used mainly for jewelry-making and ornamentation.
Ironstone
This rock is a very distinct rock with its dark red & black banding.
The black layers are magnetite and the red layers are jasper/chert.
Wanapitei Breccia from an area near Sudbury, Ontario CANADA
the breccia from this area has a distinctive appearance and is known as Wanapitei Breccia as it was quarried in the Wanapitei Lake Quarry
it is also known under the trade name of "Aylmer antique"
this breccia is composed of layers of angular blocks, often outlined in black
the lighter pinkish - peach blocks are dolomite
the darker, tan blocks are made of a mixture of quartz and plagioclase
this stone takes a fine polish.
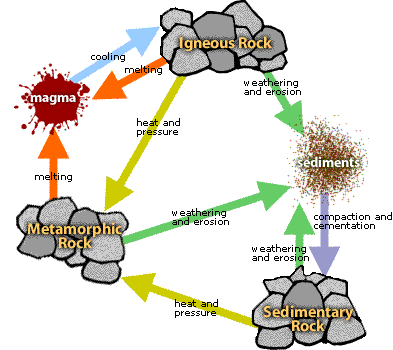
he Rock Cycle is a group of changes. Igneous rock can change into sedimentary rock or into metamorphic rock. Sedimentary rock can change into metamorphic rock or into igneous rock. Metamorphic rock can change into igneous or sedimentary rock.
Igneous rock forms when magma cools and makes crystals. Magma is a hot liquid made of melted minerals. The minerals can form crystals when they cool. Igneous rock can form underground, where the magma cools slowly. Or, igneous rock can form above ground, where the magma cools quickly.
When it pours out on Earth's surface, magma is called lava. Yes, the same liquid rock matter that you see coming out of volcanoes.
On Earth's surface, wind and water can break rock into pieces. They can also carry rock pieces to another place. Usually, the rock pieces, called sediments, drop from the wind or water to make a layer. The layer can be buried under other layers of sediments. After a long time the sediments can be cemented together to make sedimentary rock. In this way, igneous rock can become sedimentary rock.
Basalt is a very common igneous rock. In fact it is the most common rock in the Earth's crust. Almost all oceanic crust is made of basalt and basalt is a common extrusion from many volcanic regions around the world. It forms from the melting of the upper mantle and its chemistry closely resembles the upper mantle's composition. It is generally silica poor and iron and magnesium rich. Basalt originates from "hot spot" volcanoes, massive basalt flows and mid oceanic ridges.
Chalk is a sedimentary rock of biochemical origin. It is soft, white and porous. It formed in the deep ocean far from land via the gradual accumulation of the calcite shells of coccolithophores. Layers of chalk are known that are hundreds of feet thick, indicating extremely long periods of accumulation.
Note that many products called chalk are not calcite. Gypsum is a common replacement (for example the "chalks" used on blackboards), as is talc. True chalk, however, is always composed of minute crystals of calcite.
Gypsum is an evaporative sedimentary rock composed primarily of the mineral gypsum. Gypsum beds can be huge, although since it is somewhat water soluble it is unstable at the surface except in very arid regions.
Gneiss is a metamorphic rock characterized by distinct banding and relatively little mica and chlorite minerals. Gneiss resembles schist in composition and texture, but schist does not show layering or banding.
Granite is possibly the most common igneous rock type known to the general public. Granite, which is named for its "granular" or phaneritic texture, has crystals that tend to be easily seen, although they are generally small. It is a rock that has been used for centuries for many different purposes such as building material. Granite was used with limestone as a building material for the pyramids of Egypt. Its durability, beauty and abundance make it a preferred choice of stone over most others. Granite is also a source of many mineral specimens. Unfortunately, most of the crystals in a granite form anhedral crystals or crystals that lack their outward crystal shape. This is due to the way that the crystals grow into each other to form interlocking crystal frameworks. Although this gives granite its great durability, it limits its desirability as a source of mineral specimens. Occasionally there are pockets within a granite where crystals can form very nice specimens.
Soapstone is a metamorphic rock formed at tectonic subduction zones. Soapstone is primarily composed of the mineral talc whose softness results in the soapy feel of the rock (hence the name). Soapstone has been used as a carving material for thousands of years.
Slate is a low grade metamorphic rock with a fine grain. Slate often has a gray color and may be split into parallel layers. The precursor rock is generally a shale or siltstone. Slate is used as roofing, as the flat beds of billiard tables, and historically had many other uses since replaced (such as school blackboards).